Snake's head
(Fritillaria meleagris)
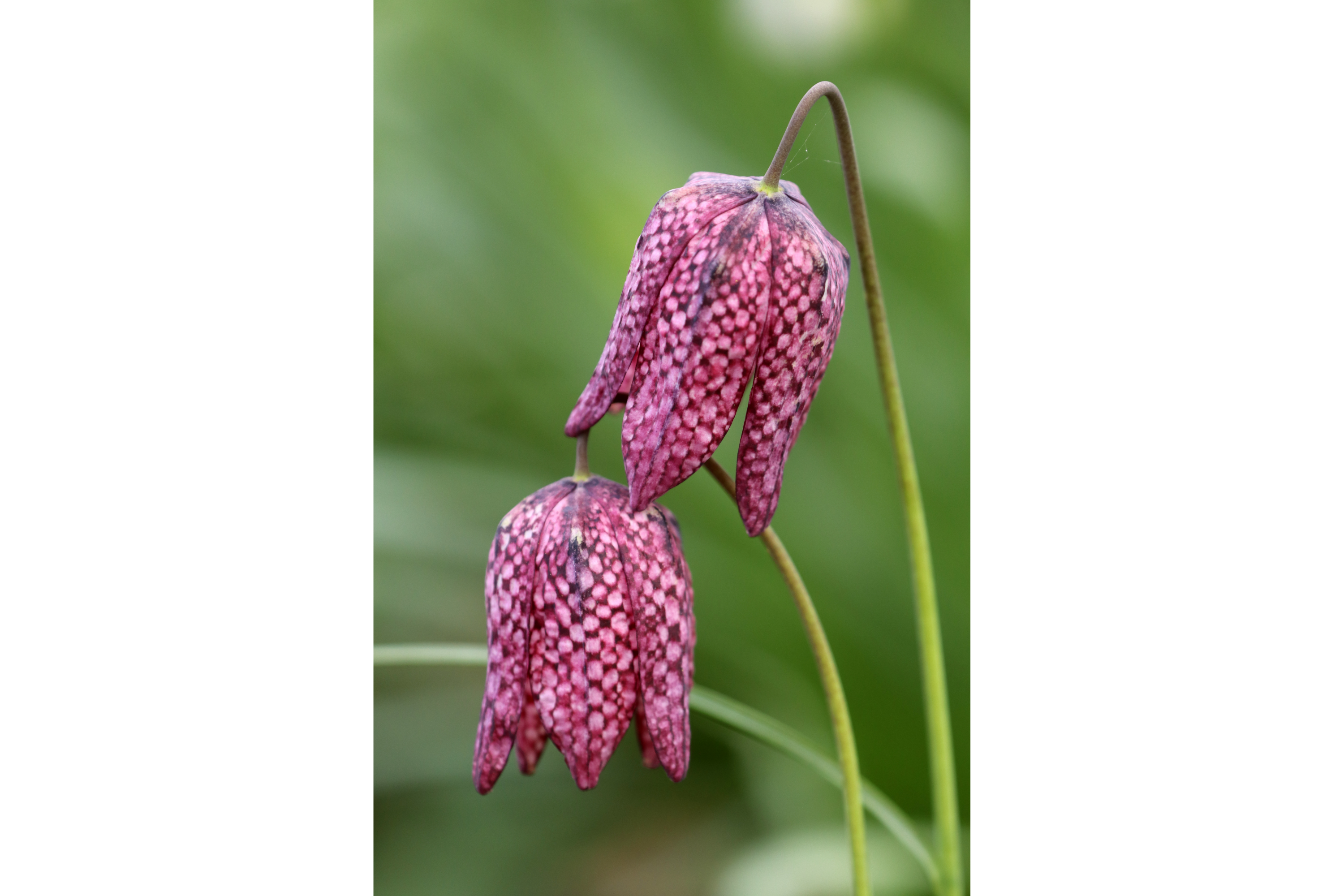

Description
Fritillaria meleagris is a Eurasian species of flowering plant in the lily family Liliaceae. Its common names include snake's head fritillary, snake's head (the original English name), chess flower, frog-cup, guinea-hen flower, guinea flower, leper lily (because its shape resembled the bell once carried by lepers), Lazarus bell, chequered lily, chequered daffodil, drooping tulip or, in the British Isles, simply fritillary. The plant is a bulbous perennial native to the flood river plains of Europe where it grows in abundance. The flower has a chequered pattern in shades of purple, or is sometimes pure white. It flowers from March to May and grows between 15–40 cm (6–16 in) in height. The plant has a button-shaped bulb, about 2 cm (0.79 in) in diameter, containing poisonous alkaloids. It grows in grasslands in damp soils and river meadows at altitudes up to 800 m (2,625 ft). Fritillaria meleagris is native to Europe and western Asia but in many places it is an endangered species that is rarely found in the wild but is commonly grown in gardens. In Croatia, the flower is known as kockavica and is associated by some with the country's national symbol. It is the official flower of the Swedish province of Uppland, where it grows in large quantities every spring in the meadows of Kungsängen (King's Meadow), just outside Uppsala, which gives the flower its Swedish name, kungsängslilja ("king's meadow lily"). It is also found for example in Sandemar Nature Reserve, a nature reserve west of Dalarö in Stockholm Archipelago.
Taxonomic tree: