Wishbone flower
(Torenia fournieri)
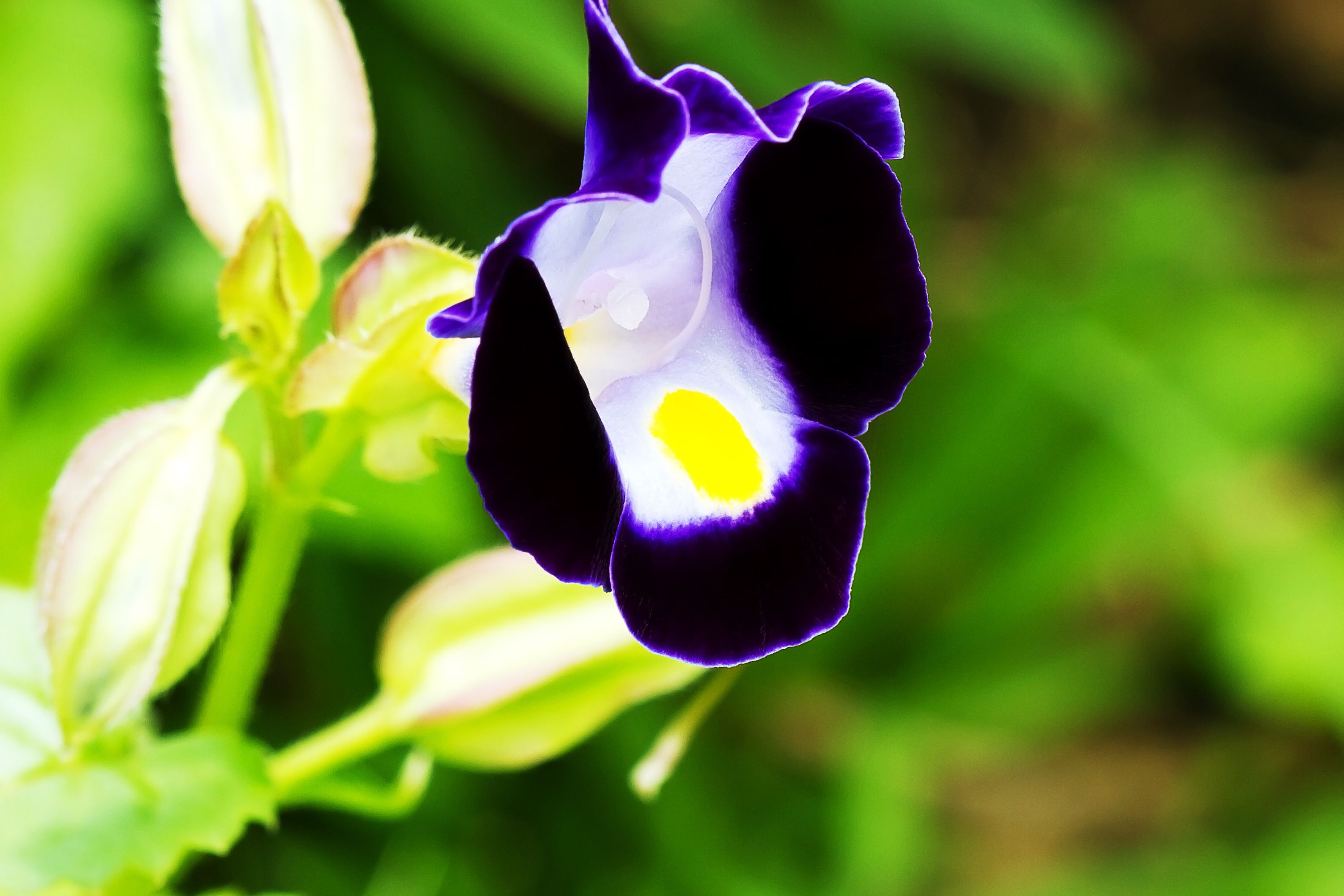

Description
Torenia fournieri, also known as the wishbone flower or bluewings, is a small, flowering plant native to Southeast Asia. This plant belongs to the family Linderniaceae and is widely cultivated for its showy flowers that come in a range of colors from blue, purple, pink, white, and yellow. In this article, we will explore Torenia fournieri in-depth, including its description, history, cultivation, and care. Description Torenia fournieri is a small, herbaceous perennial plant that typically grows up to 8-12 inches in height and spreads up to 12-18 inches in width. It has a mounding, compact growth habit with a dense, bushy foliage that is deep green and glossy. The leaves are oval-shaped, toothed at the edges, and arranged oppositely on the stem. The flowers of Torenia fournieri are trumpet-shaped and are borne on short, branching stems that emerge from the leaf axils. They typically measure about 1 inch across and have a distinctive two-lobed lower petal that gives them the appearance of a wishbone, hence the common name "wishbone flower." The flowers come in a range of colors including blue, purple, pink, white, and yellow, and are often marked with darker spots or stripes. They bloom continuously throughout the growing season, from spring to fall, and are attractive to butterflies and hummingbirds. History Torenia fournieri was first discovered in Vietnam in the 19th century by the French botanist Gustave Adolphe Louis Huleu. He named the plant after the French botanist Louis Fournier, who had collected specimens of Torenia in the Philippines. Torenia fournieri was introduced into cultivation in Europe and the United States in the late 1800s and has since become a popular garden plant, especially in warmer climates. Cultivation Torenia fournieri is a versatile plant that can be grown in a range of climates and soil types. It prefers a moist, well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter and a location with partial shade to full sun. In hot climates, it will benefit from some shade during the hottest part of the day. Propagation Torenia fournieri can be propagated from seed or by stem cuttings. Seeds should be sown indoors in early spring and kept moist until they germinate. Once the seedlings have developed several sets of true leaves, they can be transplanted into larger containers or directly into the garden. Stem cuttings can be taken in late spring or early summer when the plant is actively growing. Take cuttings from the tips of the stems and remove the lower leaves. Dip the cut end of the stem in rooting hormone and plant it in a pot or tray filled with a well-draining soil mix. Keep the soil moist and the cutting in a shaded location until roots have formed. Care Watering Torenia fournieri prefers evenly moist soil and will not tolerate drought. Water it regularly, especially during hot, dry periods, and mulch around the base of the plant to help retain moisture. Fertilizing Torenia fournieri will benefit from regular applications of fertilizer during the growing season. Use a balanced fertilizer such as 10-10-10, applied according to the manufacturer's instructions. Pruning Torenia fournieri does not require extensive pruning, but deadheading spent flowers will encourage the plant to produce more blooms. Cut back any dead or damaged foliage as needed. Pests and Diseases Torenia fournieri is generally a healthy plant, but it can be susceptible to some pests and diseases. Here are some of the most common: Powdery Mildew: This is a fungal disease that appears as a white or gray powdery coating on the leaves, stems, and flowers of the plant. It thrives in warm, humid conditions and can be prevented by keeping the plant well-ventilated and avoiding overhead watering. If the disease does occur, it can be treated with a fungicide. Aphids: Aphids are small, soft-bodied insects that can infest the plant and cause damage by sucking sap from the leaves and stems. They can be controlled by spraying the plant with insecticidal soap or neem oil. Spider Mites: Spider mites are tiny, sap-sucking pests that can cause yellowing and bronzing of the leaves. They are most active in hot, dry conditions and can be treated with insecticidal soap or neem oil. Thrips: Thrips are small, winged insects that can cause damage by sucking sap from the leaves and flowers. They can also transmit viruses to the plant. Thrips can be controlled by spraying the plant with insecticidal soap or neem oil. Leaf Spot: This is a fungal disease that appears as brown or black spots on the leaves of the plant. It can be prevented by avoiding overhead watering and keeping the plant well-ventilated. If the disease does occur, affected leaves should be removed and destroyed to prevent further spread. Root Rot: Root rot is a fungal disease that affects the roots of the plant, causing them to rot and die. It is caused by overwatering and poorly-draining soil. To prevent root rot, ensure the plant is growing in well-draining soil and avoid overwatering. If root rot occurs, the affected plant should be removed and discarded to prevent further spread.
Taxonomic tree: