Guiana chestnuts
(Pachira)
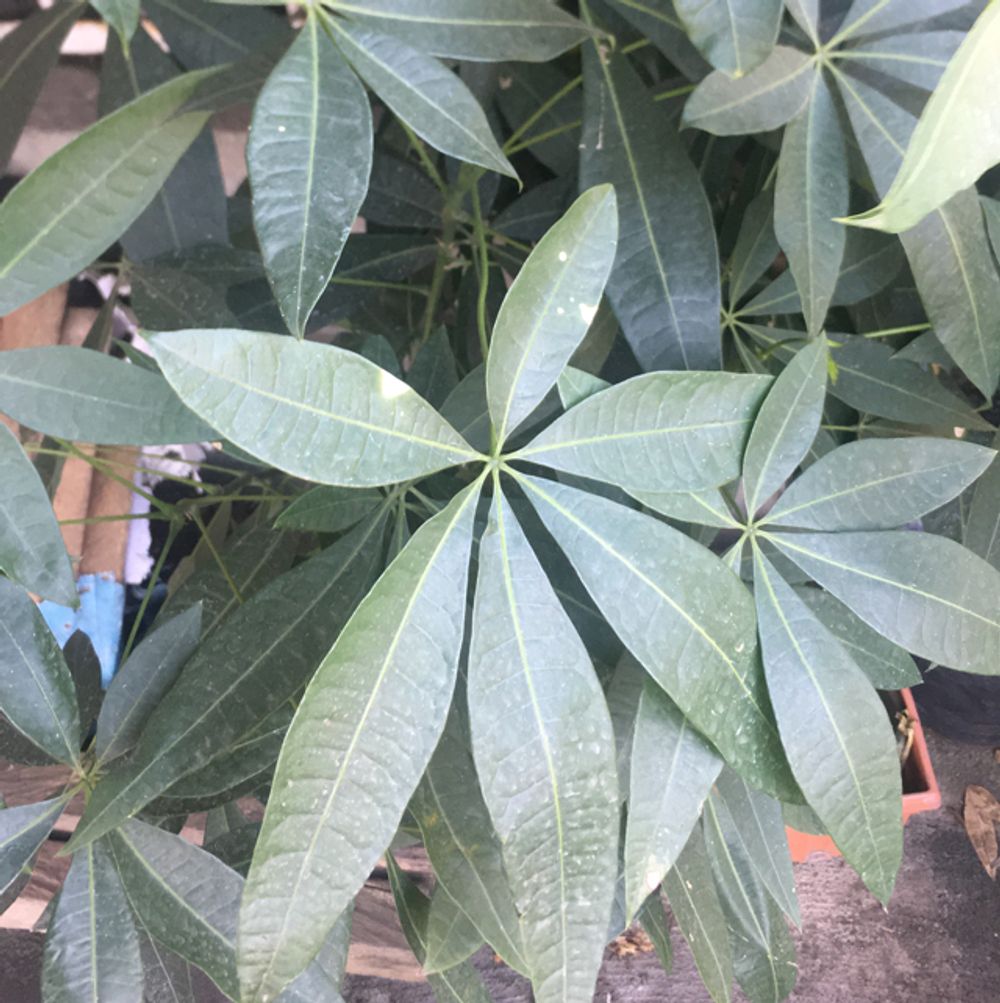

Description
Pachira plants, also known as money trees or Guiana chestnuts, are a group of trees and shrubs native to Central and South America. These plants have become popular ornamental plants due to their attractive foliage, unique braided trunk, and easy care requirements. In this article, we will explore the different aspects of Pachira plants, from their physical characteristics and growth habits to their care requirements and propagation techniques. Taxonomy and Nomenclature: Pachira is a genus of flowering plants in the mallow family (Malvaceae), which includes approximately 25 species of trees and shrubs. The name Pachira is derived from the Guyanese word "pacay," which refers to the edible fruit of the Pachira aquatica species. The Pachira genus is closely related to the Bombax and Ceiba genera, which also belong to the Malvaceae family. Physical Characteristics: Pachira plants have several distinctive physical features that make them easy to identify. These plants typically have long-stemmed, palmately compound leaves with 5 to 9 leaflets that are ovate or lanceolate in shape. The leaves are bright green and glossy, and they can grow up to 12 inches long. Pachira plants are also known for their unique braided trunks, which are the result of intertwining multiple young stems during the early stages of growth. The flowers of Pachira plants are large and showy, with five petals and numerous stamens. The flowers are typically white, pink, or red in color and are followed by round, woody fruit capsules that contain edible seeds. Pachira plants can grow up to 60 feet tall in their natural habitat, although they are typically much smaller when grown as houseplants. Growing Conditions: Pachira plants are relatively easy to care for and can thrive in a variety of growing conditions. These plants prefer bright, indirect sunlight, but they can also tolerate low light conditions. They prefer well-draining soil that is kept consistently moist but not waterlogged. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other issues, so it is important to allow the soil to dry out slightly between watering sessions. Pachira plants can also benefit from regular fertilization during the growing season, using a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer every two weeks. They also appreciate a humid environment, which can be achieved by misting the leaves regularly or placing a tray of water near the plant. Propagation: Pachira plants can be propagated through several methods, including stem cuttings, air layering, and seed germination. Stem cuttings should be taken from healthy, mature plants and rooted in well-draining soil. Air layering involves making a small cut in the stem of the plant and wrapping it in moist sphagnum moss until roots form. Seed germination can also be successful but may require some patience and skill. Uses: Pachira plants are primarily grown as ornamental plants due to their attractive foliage and unique braided trunks. However, some species of Pachira have additional uses. For example, the seeds of the Pachira aquatica species are edible and can be roasted or boiled. The bark of some Pachira species is also used in traditional medicine to treat various ailments. Conclusion: Pachira plants are a fascinating group of trees and shrubs that are prized for their attractive foliage, braided trunks, and easy care requirements. Whether grown as houseplants or in their natural habitat, these plants are sure to add a touch of tropical beauty to any setting. With their distinctive physical characteristics and versatile growing conditions, Pachira plants are a great choice for both novice and experienced gardeners alike.
Taxonomic tree: