Bog Adder's Mouth Orchid
(Hammarbya paludosa)

Description
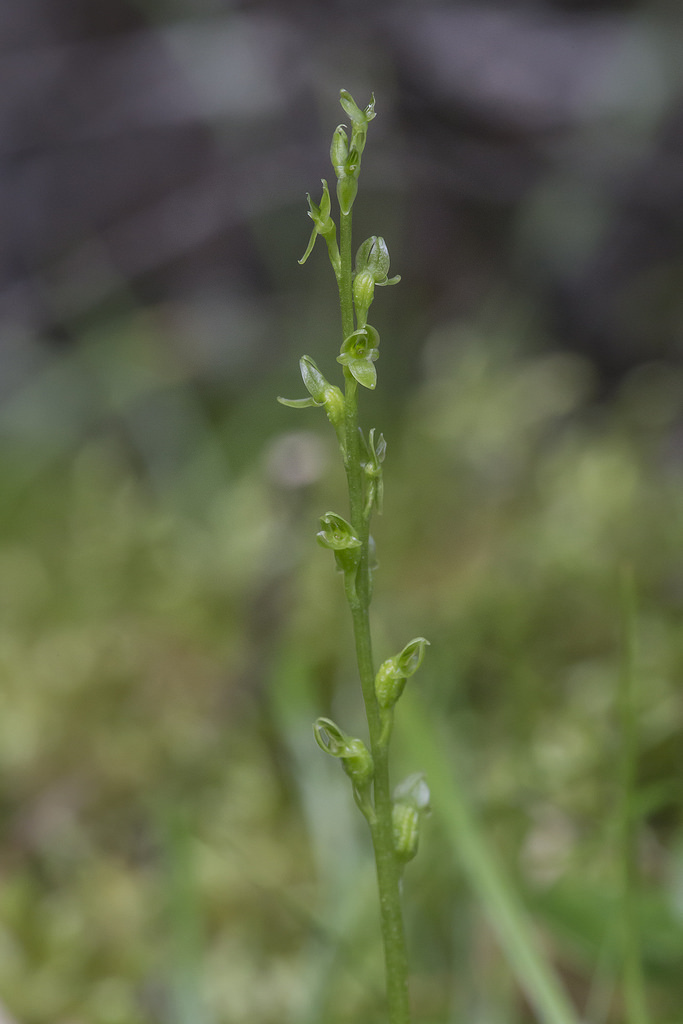
Hammarbya paludosa (or Malaxis paludosa) is a small orchid commonly known as bog orchid, bog adder's-mouth or bog adder's-mouth orchid. It grows in bogs in temperate and subarctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere. It is a small, inconspicuous orchid which can reach 15 cm in height but usually grows to between 4 and 8 cm. The stem is yellow-green, has three to five corners and grows from a small pseudobulb. There are two, three or sometimes four basal leaves. These are oval to oblong, fleshy and pale green or yellow-green. The edges and tips curve inwards. There are one to three small, scale-like leaves higher up the stem. The flowers grow in a spike-like raceme that is 1.5–6 cm long and bears up to 25 flowers. They are small and greenish, about 2 mm wide and 4 mm tall. They have three sepals and three petals, one of which is modified to form a lip. There is one dorsal sepal pointing downwards and two lateral sepals pointing up. The two normal petals are small, narrow and strap-shaped and curve back around the sepals. The short, triangular lip is dark green with paler stripes and points upwards and forwards. The flowers have a sweet, cucumber-like scent. In the majority of orchids, the flowers are resupinate, twisting 180° during development so that the lip points downwards. In Hammarbya paludosa, the flowers twist a further 180° so that the lip once more points upwards. Charles Darwin noted this feature in his 1862 book Fertilisation of Orchids.
Taxonomic tree: