Peach tree
(Prunus persica)

Description
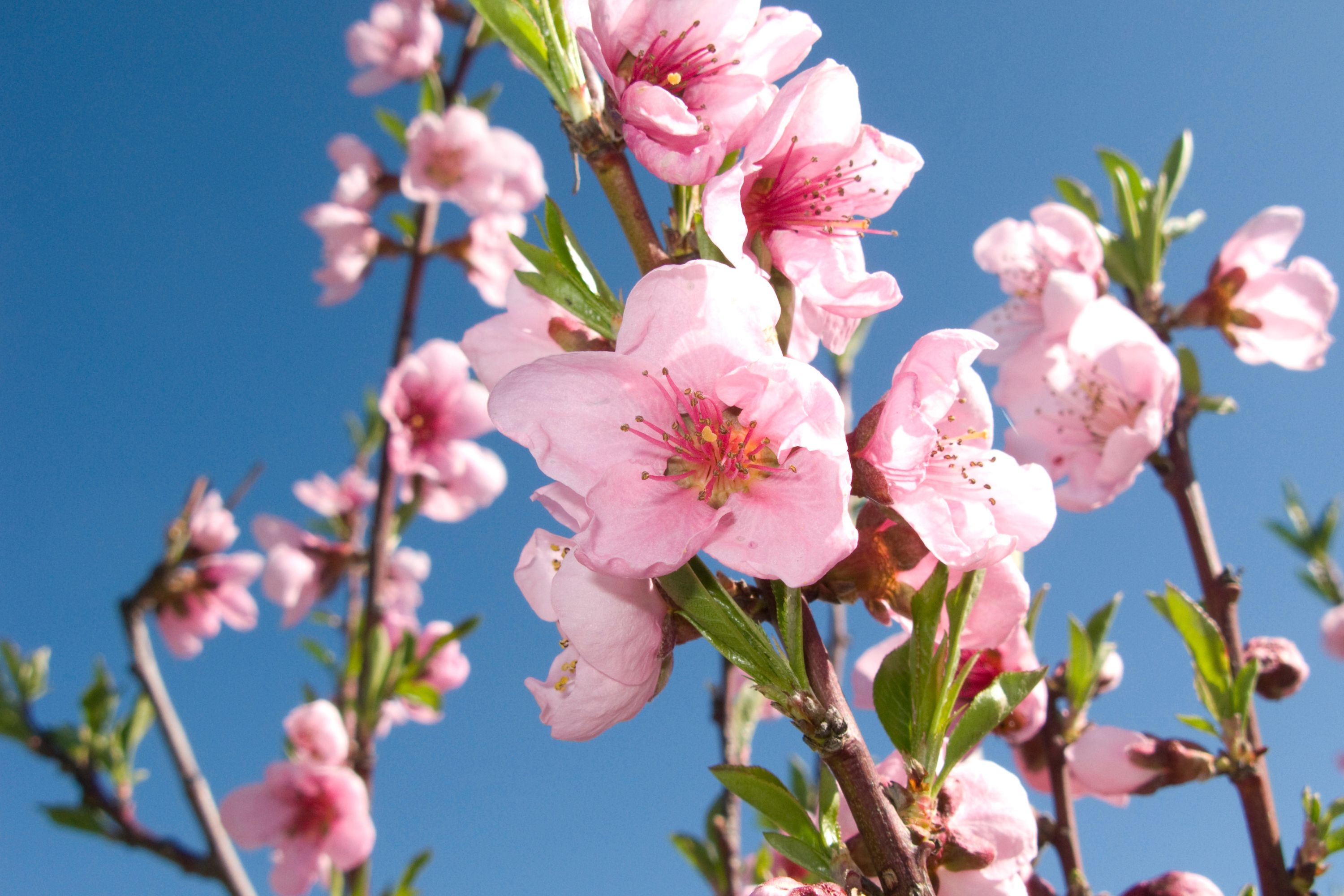
Prunus persica, commonly known as the peach tree, is a species of deciduous tree native to China, but is now widely cultivated throughout the world. It belongs to the family Rosaceae and is closely related to other fruit trees such as the cherry, apricot, and plum. The peach tree is a popular ornamental and fruit tree, prized for its beautiful flowers and delicious, juicy fruit. Description The peach tree typically grows up to 25 feet tall, although some cultivars can reach up to 30 feet. It has a round to oval-shaped crown, with branches that are covered in smooth gray bark. The leaves are lanceolate to elliptical in shape, with a serrated margin, and can grow up to 7 inches long. The tree produces beautiful pink to reddish flowers in early spring, before the leaves appear. The flowers are five-petaled and have a sweet fragrance. The fruit of the peach tree is a drupe, which means it has a single seed surrounded by a fleshy outer layer. The fruit is typically round to oblong in shape, with a fuzzy skin that ranges in color from yellow to red. The flesh is juicy and sweet, and can range in color from white to yellow to orange. Cultivation Peach trees are hardy in USDA zones 5 to 9 and require a minimum of 600 hours of chilling below 45°F to break dormancy and set fruit. They prefer well-draining soil that is slightly acidic (pH 6.0 to 6.5) and full sun exposure. Peach trees are typically propagated by budding or grafting onto rootstock, and can take 3 to 4 years to bear fruit. Peach trees require regular pruning to maintain their shape and promote fruiting. The best time to prune is in late winter or early spring, before new growth begins. The goal of pruning is to create an open, vase-shaped canopy that allows sunlight and air to reach the interior of the tree. Pests and Diseases Peach trees are susceptible to a number of pests and diseases, including peach tree borers, Oriental fruit moths, and bacterial spot. Peach leaf curl, caused by the fungus Taphrina deformans, is a common disease that causes the leaves to curl and turn red. It can be controlled with fungicides, but prevention through good sanitation and site selection is the best approach. Harvest and Use Peaches are typically harvested in mid- to late summer, when the fruit is fully ripe and the flesh is soft. The fruit should be picked gently to avoid bruising or damaging the skin. Peaches can be eaten fresh, canned, or used in a variety of baked goods such as pies and cobblers. They are also a popular ingredient in jams, jellies, and preserves. Varieties There are hundreds of different peach cultivars, each with its own unique characteristics. Some popular varieties include: Elberta: A yellow-fleshed peach with a red blush. It is a late-season variety and is one of the most widely grown cultivars in the United States. Redhaven: A yellow-fleshed peach with a red skin. It is an early-season variety that is highly productive and disease-resistant. Hale: A white-fleshed peach with a red skin. It is a mid-season variety that is highly prized for its sweet, juicy flavor. Conclusion Prunus persica, or the peach tree, is a popular fruit tree that is prized for its delicious, juicy fruit and beautiful pink flowers. With proper cultivation and care, peach trees can provide years of enjoyment and delicious fruit. Whether eaten fresh, canned, or used in baked goods, peaches are a beloved fruit.
Taxonomic tree: