What gives pine trees that fresh scent?
The distinctive fresh scent of pine trees is primarily due to the presence of volatile organic compounds, specifically terpenes, which are emitted by the trees.
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds produced by many plants, including conifers like pine trees. The most notable terpene responsible for the classic pine scent is alpha-pinene, which is found in high concentrations in pine needles, bark, and resin.
Alpha-pinene is a monoterpene that has a characteristic woody, resinous, and fresh aroma. It’s also found in other plants such as rosemary, eucalyptus, and juniper. When you walk through a pine forest or crush pine needles in your hands, you release these volatile terpenes into the air, creating that distinctive fresh scent we associate with pine trees.
In addition to being pleasant to our senses, these compounds also serve a purpose for the trees themselves. Terpenes play a role in protecting the trees from herbivores and pathogens, as well as helping to reduce water loss during periods of drought.
More about alpha-pinene
As the most abundant terpene in nature, alpha-pinene is found in various plant species, but it is particularly prominent in conifers like pine trees, as well as in other plants like rosemary, eucalyptus, and juniper.
Chemically, alpha-pinene is a monoterpene, meaning it is composed of two isoprene units, and has the molecular formula C10H16. There are two structural isomers of pinene, alpha-pinene, and beta-pinene, with alpha-pinene being the most common of the two.
Apart from its characteristic scent, alpha-pinene also possesses a range of biological properties, some of which include:
Anti-inflammatory
Research has shown that alpha-pinene exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, making it potentially useful for managing conditions like asthma, arthritis, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Antibacterial and antifungal
Alpha-pinene has demonstrated antibacterial and antifungal activity, which could be harnessed for potential therapeutic applications.
Antioxidant
The compound has shown antioxidant properties, which can help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Insect repellant
The strong scent of alpha-pinene can act as a natural insect repellant, deterring pests from attacking plants that produce it.
Memory and cognitive enhancement
Some studies suggest that alpha-pinene may have positive effects on memory and cognitive function, although more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Alpha-pinene plays a crucial role in the plant’s defense mechanisms, deterring herbivores and protecting against pathogens. In addition, its release into the atmosphere can help reduce water loss in plants during drought conditions.
In summary, alpha-pinene is a fascinating compound with a wide range of biological properties and uses. Its prevalence in nature, especially in conifers like pine trees, is responsible for the iconic pine scent we all know and love.
More about pine trees
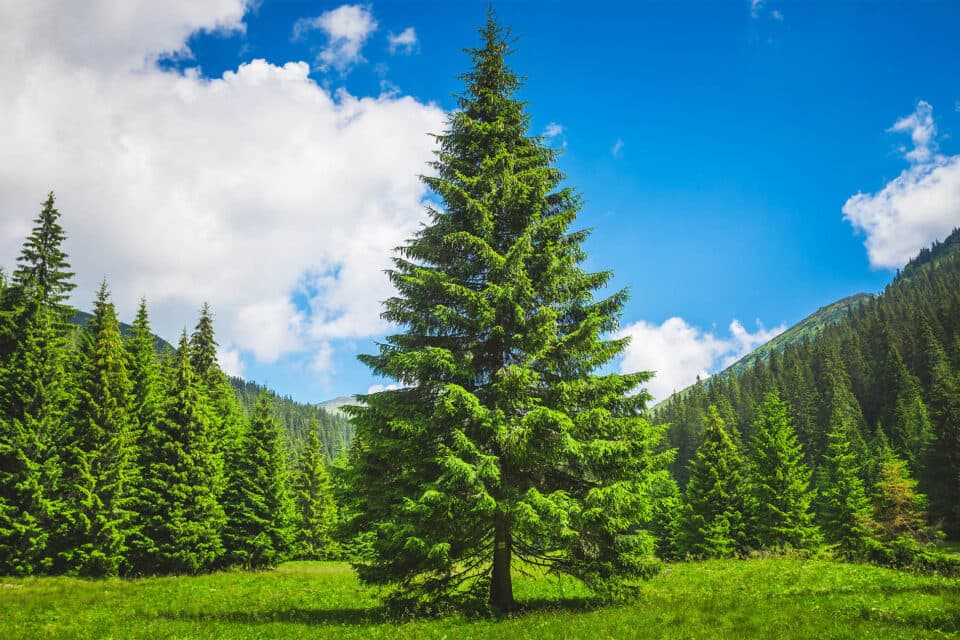
Pine trees have been adorning landscapes and igniting the imagination of nature lovers for centuries. These evergreen conifers belong to the family Pinaceae and the genus Pinus, which comprises over 120 species native to the Northern Hemisphere.
Ecology and Distribution
Pine trees are well-adapted to a range of climates, from the snowy mountains of the Alps to the arid deserts of the American Southwest. These hardy trees can grow in different types of soils, and their strong roots help prevent erosion. They thrive in areas with full sunlight and well-drained soil, making them a valuable component of many ecosystems.
One of the most recognizable features of pine trees is their needle-like leaves, which are arranged in bundles, called fascicles. These leaves can remain on the tree for years, giving pines their evergreen appearance. Pine cones, the tree’s reproductive structures, also come in various shapes and sizes, depending on the species.
Pine trees play a vital role in the forest ecosystem. They provide habitat and food for numerous species, such as squirrels, birds, and insects. In turn, these animals assist in the dispersal of pine seeds, ensuring the continuation of the species.
Cultural Significance
Throughout history, pine trees have been revered in various cultures for their beauty, resilience, and practical uses. In ancient Rome, the pine tree was a symbol of the goddess Diana, associated with fertility and the moon. The Celts viewed pines as a sign of wisdom, while Native Americans used pine needles in traditional basket weaving and as medicine.
In Japan, the pine tree is a symbol of longevity and prosperity. This is evident in their New Year’s tradition of decorating the entrances of homes with kadomatsu, an arrangement that includes pine branches, bamboo, and plum blossoms. The pine tree also plays a central role in the Japanese art of bonsai, where miniature versions are meticulously crafted to reflect the essence of their full-sized counterparts.
Practical Uses
Pine trees have long been a valuable resource for humans. The wood, known for its durability and resistance to decay, is commonly used in construction, furniture making, and as a source of pulp for paper production. Additionally, pine resin has been used to create products such as turpentine, rosin, and pitch, which have applications in the paint, adhesive, and pharmaceutical industries.
The versatile nature of pine trees also extends to their culinary and medicinal uses. Pine nuts, the seeds found within the cones, are a delicious and nutritious treat, often used in Mediterranean cuisine, especially in pesto sauce. Pine needles can be brewed into a vitamin C-rich tea, which has been used traditionally to ward off scurvy and colds. The essential oil derived from pine needles also offers anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
Conservation and Sustainability
Despite their resilience, pine trees face threats from climate change, deforestation, and invasive species. Climate change impacts the distribution and growth of pine trees, leading to a decline in some species and an increase in forest fires. Deforestation for agriculture and urbanization reduces the available habitat for pine trees and the wildlife that depends on them.
As responsible stewards of the environment, it is crucial that we manage our forests sustainably and support conservation efforts. This includes promoting responsible logging practices, reforestation projects, and habitat preservation.
Conclusion
Pine trees are truly remarkable for their beauty, adaptability, and versatility. They have played a significant role in the culture
and history of many societies, and they continue to inspire us with their evergreen presence. As we stroll through pine forests or admire a single tree standing tall in the landscape, we can appreciate the myriad of ways in which these natural wonders contribute to our lives.
By understanding the ecology, cultural significance, and practical uses of pine trees, we can foster a deeper connection with these majestic giants. Moreover, this connection can inspire us to be more mindful of our impact on the environment and to take steps to ensure the survival of these invaluable species for generations to come.
So the next time you find yourself in the presence of a pine tree, take a moment to appreciate the complex beauty it represents, and maybe even share some of the fascinating tidbits you’ve learned from this article. After all, a little bit of pine tree knowledge goes a long way in helping us stay rooted in our appreciation for the natural world around us.
—
Check us out on EarthSnap, a free app brought to you by Eric Ralls and Earth.com.